How to Reconstitute Peptides Using BAC Water
Feb 11th 2026
In the United States, therapeutic peptides support many modern medical research practices. Research peptides also assist laboratory teams during controlled experimental treatment planning. Correct peptide reconstitution protects users from dosing errors during laboratory procedures. Lyophilized powders require careful handling during initial liquid mixing processes. Improper mixing may cause unstable solutions with reduced biological effectiveness. Researchers must follow careful steps to protect peptide quality and solution safety.
BAC water remains a common choice for multi-dose peptide mixing procedures. This water contains preservatives that reduce bacterial growth inside opened vials. Preservatives help maintain safety during repeated vial access sessions. Sterile handling supports accurate dosing and reduces contamination risks significantly. Many facilities require documented reconstitution practices for consistent laboratory results. Clear preparation methods help reduce handling mistakes during daily research activities. Lab staff prefer simple methods that improve repeatable solution preparation results.
Clear methods reduce confusion during injection preparation tasks within busy labs. Researchers benefit from stable solutions prepared using reliable sterile water sources. Multi-dose use requires careful storage and handling during repeated vial access. Controlled steps help maintain peptide structure during mixing and storage practices. Training improves staff confidence during reconstitution of sensitive peptide compounds. Careful preparation protects peptide effectiveness during clinical research applications. Following methodical steps improves overall laboratory safety and preparation accuracy.
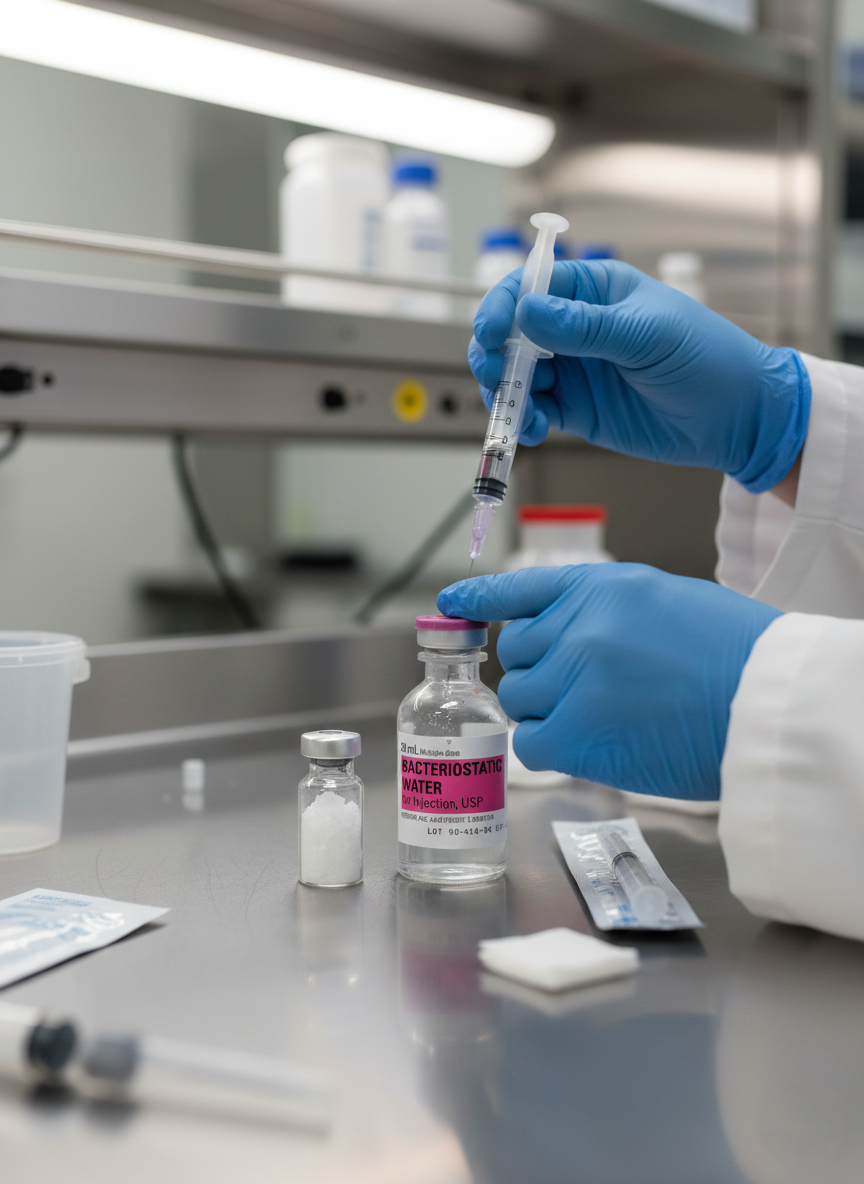

Supplies Needed
Proper supplies ensure safer handling during accurate peptide reconstitution procedures. Simple tools improve control during mixing and injection preparation activities. Using correct items helps protect peptide quality during careful solution handling.
Peptide Vial (Lyophilized Powder)
Peptides arrive as dry powders sealed under strict sterile laboratory conditions. Always confirm the peptide milligram content from the vial label clearly. Check documentation to ensure correct identification before beginning mixing steps. Proper labeling prevents dosing mistakes during repeated solution preparation processes. Vial integrity protects peptide purity during long storage periods.
Damaged vials may compromise peptide quality and stability during handling. Always inspect vial seals before beginning any mixing procedures carefully. Keep vials clean during preparation to reduce contamination risks. Store unopened vials according to provided storage guidance instructions. Controlled storage preserves peptide stability during extended holding periods.
BAC Water (Bacteriostatic Water)
BAC water supports safe multi-dose use during peptide mixing procedures. Preservatives reduce bacterial growth during repeated vial access events. This feature supports extended use without rapid contamination risks. Such distinction from other diluents is explained in guides comparing bacteriostatic water vs reconstitution solution. Store unopened water vials in clean and controlled environments. Avoid touching vial openings during any injection preparation procedures.
Always use sterile tools during water extraction steps. Do not reuse contaminated water vials for future mixing tasks. Replace water vials when contamination risks appear visually present. Clear water appearance indicates safer handling during preparation sessions. Follow sterile techniques during every extraction and injection step.
Syringes, Needles & Alcohol Swabs
Sterile syringes support accurate measurement during peptide reconstitution steps. Proper needles help deliver measured water volumes into peptide vials. Alcohol swabs disinfect vial stoppers before needle contact. Surface cleaning reduces bacterial transfer during preparation tasks. Always use fresh swabs for every vial contact point.
Dispose used needles according to facility safety protocols immediately. Sharp safety containers protect staff from accidental needle injuries. Clean preparation surfaces reduce contamination during repeated preparation cycles. Sterile tools support consistent outcomes during daily laboratory activities. Proper disposal practices maintain clean and safe working environments.
Calculating Correct Water Volume
Correct calculations ensure stable concentration during peptide reconstitution processes. Accurate volumes support reliable dosing during repeated injection preparation steps. Simple calculations help maintain consistent concentration for research applications.
Understanding Peptide Strength (mg per vial)
Check the vial label to confirm peptide strength clearly. Many vials contain measured amounts like five milligrams per vial. Knowing strength helps determine how much water to add safely. Strength guides the final solution concentration during preparation planning. Incorrect strength assumptions may cause inaccurate dosing risks. Careful review prevents costly preparation errors during mixing steps.
Document strength values for consistent laboratory record keeping. Clear records help track preparation methods across different staff members. Consistent documentation improves team accuracy during repeated preparations. Always confirm strength before calculating final solution volumes.
Deciding Desired Dosage
Decide how concentrated the final peptide solution should remain. Higher concentration supports smaller injection volumes during research dosing. Lower concentration supports gradual dosing for sensitive research applications. Desired dosage determines how much water to use. Planning dosage helps control final solution concentration safely. Discuss dosage targets with supervisors before mixing peptide solutions.
Clear goals support safe injection preparation during research trials. Consistent dosage improves repeatable results during peptide use. Avoid guessing dosage to prevent unwanted concentration variations. Use documented guidelines to guide dosage planning decisions.
Basic Reconstitution Calculation Method
Use a simple formula to determine required water volume.
- Divide peptide amount by desired concentration to calculate water volume.
- Ten milligrams divided by two milligrams equals five milliliters.
This method supports accurate peptide reconstitution during mixing tasks. Clear calculations reduce measurement errors during preparation activities. Always double check calculations before injecting water into vials. Confirm values with colleagues to reduce human calculation mistakes. Accurate volume improves consistent dosing during injection preparation tasks. Incorrect volume may weaken or overly concentrate peptide solutions. Record calculated volumes within laboratory preparation documentation logs.

Proper Mixing Technique
Disinfect the vial stopper using a clean alcohol swab thoroughly. Draw the calculated BAC water volume into a sterile syringe. Inject water slowly down the vial wall during mixing. Slow injection reduces foam formation during solution preparation steps. Foam may damage sensitive peptide structures during mixing processes. Gently swirl the vial to dissolve the powder evenly. Avoid shaking vigorously to protect peptide structural integrity.
Gentle movement helps dissolve powder without introducing air bubbles. Air bubbles may reduce dosing accuracy during injection preparation tasks. Swirling encourages uniform solution formation during careful mixing procedures. Observe the solution until powder dissolves completely. Cloudy solutions may indicate incomplete mixing or contamination risks. Allow time for full dissolution before preparing injections. Patience supports stable solutions during peptide reconstitution activities. Careful technique protects peptide performance during clinical research use.
Storing Reconstituted Peptides
Store reconstituted peptides inside refrigerators between two and eight degrees. Cold storage helps preserve peptide stability during extended holding periods. Proper refrigeration slows degradation of sensitive peptide compounds. Label vials with reconstitution dates for safe tracking purposes. Use aseptic technique during every vial access event. Repeated access increases contamination risks without proper sterile handling. Keep vials sealed tightly between uses to reduce contamination. Many peptides remain stable for several weeks when refrigerated properly. Storage stability depends on peptide type and handling quality.
Certain peptides like BPC-157 require careful cold storage handling. Other peptides such as TB-500 also benefit from controlled refrigeration. Avoid freezing solutions unless manufacturer guidance allows freezing safely. Freezing may damage peptide structure during temperature fluctuations. Monitor solution clarity before each injection preparation activity. Discard solutions showing cloudiness or color changes immediately. Always follow facility storage protocols during multi-dose usage. Document storage conditions for consistent laboratory quality control. Controlled storage improves repeatable outcomes during peptide research use.
Conclusion
Accurate peptide reconstitution depends on careful calculation and sterile technique. Correct supplies support safe handling during repeated preparation activities. Using BAC water helps reduce contamination during multi-dose vial usage. Gentle mixing protects peptide structure during solution formation steps. Cold storage preserves peptide stability during extended research use. Systematic preparation supports reliable results during clinical research activities. Careful planning reduces dosing errors during injection preparation practices. Stable solutions improve confidence during therapeutic peptide research handling. Clear methods help teams maintain consistent preparation outcomes daily. Safe handling supports better research quality and patient safety practices.
Strong preparation habits support safer research handling across clinical environments. Clear calculations help protect solution strength during daily laboratory use. Proper tools improve consistency during every peptide reconstitution process. Reliable storage practices protect valuable peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500.