How to Choose the Right Syringe Size
Posted by Arpovo Health on Mar 16th 2023
There are various sizes of syringes which many people are usually confused about. You might be asking about the one you would prefer to use medicine, treatment or injection method. The selection of the syringe can be essential because it directly affects the safety, accuracy, and comfort. Knowing the size of syringes, you can make the treatment process comfortable, prevent unnecessary complications. The given blog will lead you through a step by step approach, helping you to grasp insulin syringe selection, tuberculin syringe usage, and other considerations more readily.
Understanding Syringe Sizes
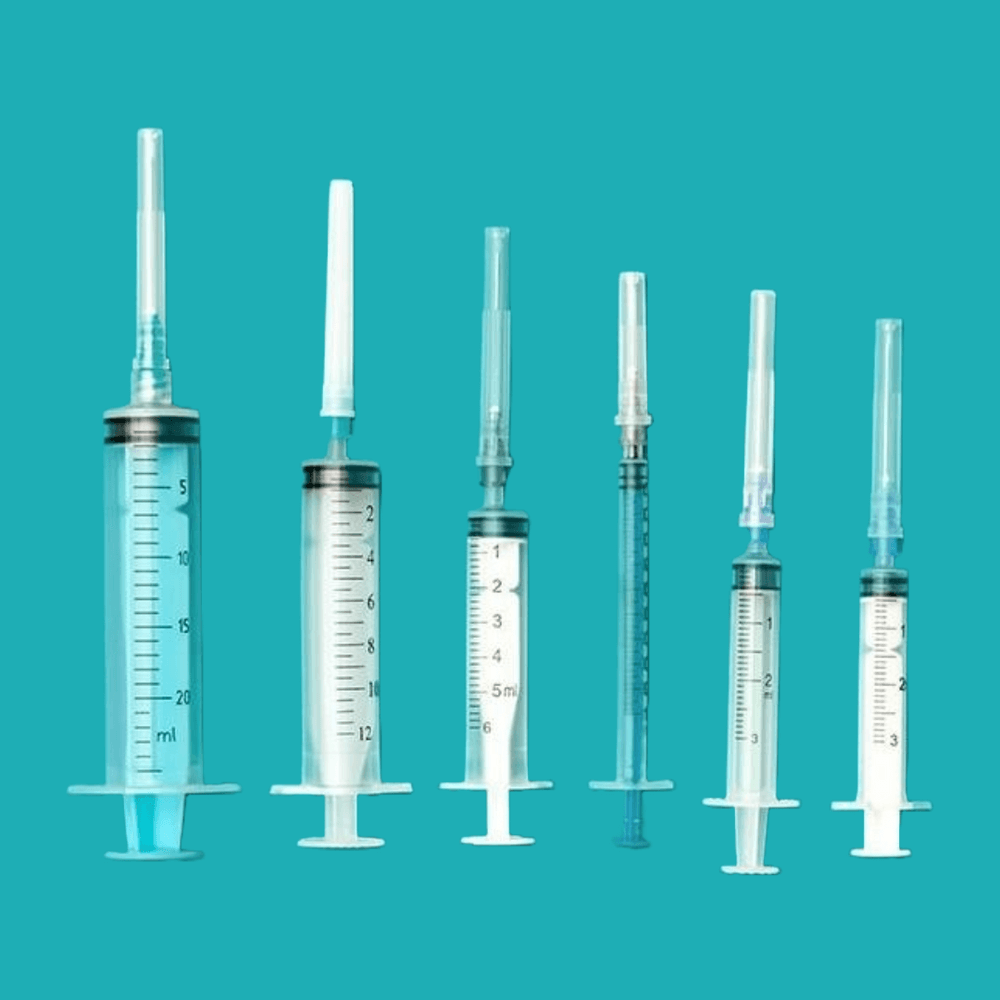
Syringes come in different sizes and their sizes are measured in millilitres (mL). They come most often in 1 mL, 3 mL, 5 mL, 10 mL, and larger sizes with specific medical use. It works better with smaller syringes when it involves accuracy in dosing the medication. Larger ones are more useful when higher volumes of fluid must be delivered at once.
A syringe-size chart is used by healthcare workers in attempting to find the right size of syringe that matches the treatment. Indeed, length of syringe used in children and adults can differ significantly since smaller and more accurate dosages are required in children. The larger sizes will be required by adults depending on the medication volume. By checking these options carefully, you ensure comfort and reduce mistakes during injections.
There are also various syringe barrels that you can experiment with in order to suit you. Some are long and wide to accommodate more, and there are others, which are small and narrow, to accommodate small amounts of medicine.
How Does Syringe Size Affect Injections?
The size of the syringe influences both the dosage and the overall injection experience. Let’s look at some common uses:
- Smaller syringes (1–3 mL): Useful for accurate dosing such as insulin or paediatric treatments. They also play a role in selecting syringes in the case of allergy tests which inject very small doses.
- Medium syringes (5–10 mL): Usually used in vaccines or as an intramuscular injection. They are best when the intramuscular syringe size has to be balanced between volume and patient comfort.
- Larger syringes (20 mL or more): These are commonly utilized in hospitals. They are used to aid in the flushing of IV lines or to draw body fluid and are essential in intravenous syringe selection.
The size of the syringe used matters in terms of the ease when the medicine gets into the body. Smaller ones induce less pain yet require more time to reach larger doses. Larger ones act faster but can become painful or irritating in case of improper use.
Key Components of Syringes
All syringes, with whatever size, possess three important parts:
- Barrel: Holds the medication or fluid.
- Plunger: Used to push or pull the fluid inside the barrel.
- Needle: Pierces the skin or vein for injection.
Depending on the requirement, various kinds of needles can be attached to syringes. They can be hypodermic needles, pen needles or syringes that already have needles in them. One must also learn how to select syringe gauge and length as the thickness of a needle varies with gauge, and the length determines how deeply the needle goes into the body.
In case of more precise medicines like insulin, you can opt to employ a smaller needle to reduce pain. The more in-depth injections, on the other hand, might need a larger needle, as well as the properly sized syringe.
Mechanisms of Action in Detail
Syringes function by creating negative pressure inside the barrel. When you pull the plunger backward, the medication is drawn inside. This expels the medicine into the body once you push the plunger forward.
Certain syringes, such as piston syringes, are designed for precise movements. They maintain the smooth controlled passage of medicine, which are significant to delicate treatments like tuberculin syringe uses. By offering gentle pressure and accurate dosing, these designs minimise the chance of errors or discomfort.
Understanding this mechanism also helps with the correct size of syringe for medication, as the right size and pressure combination ensures better treatment results.
How to Use Syringes Effectively
There are a number of steps that are important in safe syringe use:
- Wash and sanitise hands and handle carefully.
- Check to find cracks, contamination or damage in the syringe.
- Securely attach the right needle type.
- Slowly and carefully draw medication, monitoring the line of dosage.
- It is important to keep the needle sterile, there should be no contact with any surface.
- Use the approved sharps containers correctly to dispose of syringes.
By selecting sterile disposable syringes, you decrease the risk of infection and contamination. They are single use and serve to keep the safety levels as high as possible. These are designed for single use and help maintain maximum safety. Always avoid reusing them, even for personal use.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Syringe Size
Selecting the correct syringe offers multiple benefits, especially when combined with the right needle:
- Ensures correct dosage delivery.
- Minimises discomfort during injection.
- Reduces chances of tissue injury.
- Improves safety for patients and healthcare professionals.
It is particularly necessary to match the syringe to the proper treatment when selecting insulin syringes or to select the subcutaneous syringe size. Each case requires unique precision to ensure comfort and effectiveness.
Potential Risks of Incorrect Syringe Size
Using the wrong size of syringe can lead to several risks:
- Incorrect dosage delivery.
- Increased injection pain and irritation.
- Greater chance of infection or injury.
- Higher wastage of medication.
For example, using a syringe that is too large for a child’s dose may result in overdose or wastage. Likewise, using a small syringe for large medication volumes can cause patient discomfort and extend injection time. Proper attention to syringe size for children vs adults helps prevent such issues.
Choosing the Right Syringe Size
When selecting the correct syringe, there are a number of facts to consider.
- Medication type and dosage: Some drugs may have to be taken in exact doses. An injection syringe size chart helps find the correct fit. Drugs with high volume will usually require a big barrel to administer.
- Injection method: The size of a subcutaneous over intramuscular syringe is less because each injection requires different levels of depth and accuracy.
- Needle type: It is important to choose syringe length and gauge properly to prevent any inaccuracy and a painful experience. A heavier gauge can be very uncomfortable, whereas the thinner one can fail to perform well.
- Patient factors: Consider age, weight, and medical condition. This becomes important in deciding syringe size for children vs adults because dosage needs vary.
Also, pay attention to special cases such as choosing a syringe for allergy testing, where only very small doses are needed. In larger procedures of the hospital, the choice of intravenous syringe might include bigger barrels. Taking into consideration all these points, medical workers, and patients might prevent risks and increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate size of the syringe is not by mere choice. It is concerned with safety, comfort, and providing the right amount of medicine. Choosing well gives you less pain, better accuracy, and improved treatment results. It is either insulin syringe selection, size of subcutaneous syringe, or intravenous syringe selection; the objective is the same: safe and effective care.
Considering the dosage, procedure of injection, patient needs and suitable mix of needles, you will have constant results every time. Applying the correct selection of syringes not only enhances positive health outcomes but also prevents unnecessary health and safety risks to patients and care givers.
Looking for high-quality medical supplies? Explore Arpovo Health’s full syringe and needle catalogue to find the right fit for your needs.
FAQs
How do I know which syringe size is correct for my medication?
The right syringe size depends on your medication dose and injection type. Most prescriptions in the UK carry syringe size instructions. An example would be 1ml syringes are used with insulin and 2ml to 5ml syringes are typical of vaccines or antibiotics. To avoid the risk of mistakes in dosage, always follow your GP or pharmacist.
What does syringe gauge mean and how does it affect injections?
The thickness of the needle is measured by the gauge. The larger the gauge, the thinner the needle. An example is a 31G insulin needle is very fine and painless whereas a 21G needle is thicker and is used when injecting the skin. The appropriate selection of the gauge makes the process comfortable and correct.
Can I use the same syringe for different types of injections?
No, one should not reuse syringes with different drugs. The NHS guidelines in the UK highly discourage the reuse of syringes because it has the downside of exposing a person to the danger of infection and improper dosing. Inject with a new sterile syringe with each injection.
Why are insulin syringes smaller than other syringes?
The small doses of insulin are typically measured in units and not in millilitres, thus insulin syringes are supposed to be portable, and fine needles are used frequently. Being smaller can reduce pain and also precise dosing is critical to a diabetes patient.
What risks come with using the wrong syringe size?
Using the wrong syringe can cause incorrect dosing, tissue damage, or painful injections. For example, using a syringe that’s too large may lead to underdosing, while a needle that’s too short may not reach the correct tissue. According to UK medical safety reports, medication errors linked to syringes account for nearly 10% of injection-related incidents. Always match the size of the syringe to your prescription.