How to Choose the Right Bacteriostatic Water for Injections?
Jan 28th 2026
Each injection begins with preparation, and such preparation determines the safety, accuracy and patient outcomes. In America, healthcare professionals are involved in injecting patients daily in hospitals, clinics, and home care. The selection of appropriate bacteriostatic water prevents the possibility of contamination and dosing error during injections. Health facilities depend on proper preparation solutions to ensure consistent safety and effective treatment. Millions of injections are administered every day across the United States in both clinical and personal healthcare settings. There is a need to prepare each injection carefully to prevent risks associated with the improper selection of solutions.
Understanding the choice of correct bacteriostatic water can save patients and support professional standards. Caregivers also benefit from understanding solution differences during home-based injection procedures. Selecting the right option enhances efficiency while ensuring compliance with medical safety standards. This knowledge helps reduce errors during drug mixing and injection delivery processes.
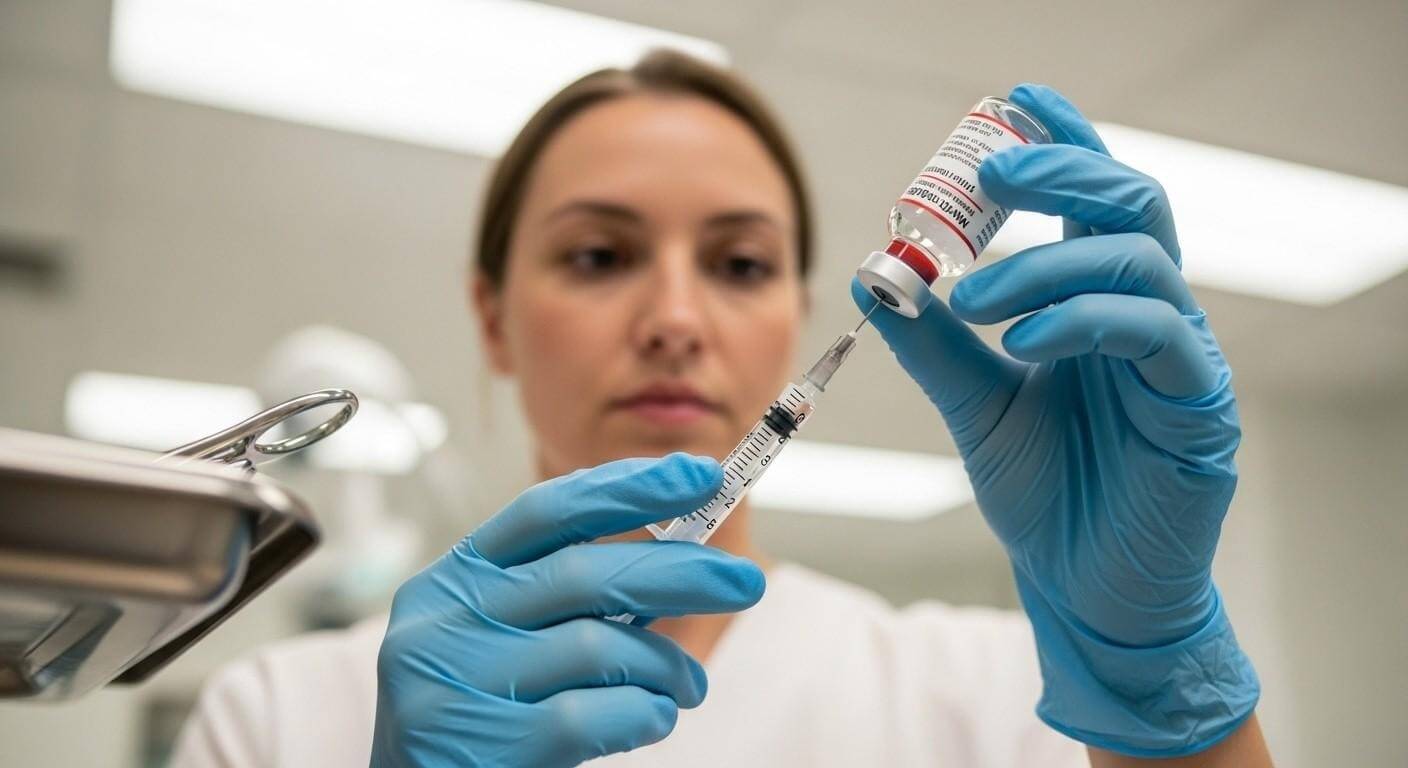
What Is Bacteriostatic Water?
Bacteriostatic water is sterile water that is used to prepare injections and to mix drugs. It has a preservative that does not allow bacteria to develop once the container is opened. This preservative allows repeated use when correct aseptic techniques are strictly followed. Unlike plain sterile water, this solution supports safer repeated withdrawals from one container. Healthcare providers typically incorporate its use as injection diluent when preparing a medication. It is vital even in cases where medication must be diluted properly before administration. A great number of injectable medicines are dependent on bacteriostatic water to reconstitute and be administered.
Understanding Multi-Dose Vials
Manufacturers package multi-dose vials to allow repeated access without rapid contamination risks. This format suits clinics handling frequent injections throughout daily medical operations. Multi-dose vials are both convenient and minimize waste of materials in long-term care facilities. Aseptic handling is an indispensable requirement when making any withdrawals from these containers. Correct technique ensures each dose remains safe for patient use. This approach supports efficiency while maintaining patient safety standards.
Role of Preservatives in BAC Water
Preservatives inhibit bacterial growth once the vial seal has been punctured. This feature distinguishes bacteriostatic water from preservative-free sterile alternatives. The preservative extends safe usability within approved clinical guidelines. This quality helps when multiple doses are prepared from one container. The preservative does not replace sterile handling or safe injection practices. Careful use remains necessary despite antimicrobial protection. Many professionals refer to this solution as BAC water selection during preparation discussions.
USP Grade and Authenticity Checks
Healthcare providers in the United States prioritize verified quality during medical solution procurement. USP grade water meets strict purity and safety standards for injectable use. These standards ensure consistent formulation, sterility, and acceptable preservative concentrations. Clinicians check labels carefully to confirm verified manufacturing and compliance. Authenticity verification reduces risks associated with counterfeit or substandard medical supplies. Professionals often rely on trusted suppliers when choosing bacteriostatic water. Clear certification helps maintain confidence during medication preparation procedures. Using verified USP grade water supports patient safety and regulatory compliance. Once opened, correct handling preserves the solution’s intended protective qualities.
Safety Guidelines Before Use
Proper handling prevents contamination during preparation and injection processes. Healthcare teams follow aseptic techniques when withdrawing solutions from containers. Sterile syringes must always be used for every withdrawal. Needle tips should never touch non-sterile surfaces during preparation. Clinicians discard solutions showing cloudiness or visible particles immediately. Preservatives reduce bacterial growth but never eliminate contamination risk entirely. Training helps staff maintain consistency during repeated solution handling. High-volume environments require strict protocols to prevent cross-contamination events. Safe practices protect both patients and healthcare workers during routine injections.
Choosing the Correct Injection Diluent
Not every medication requires bacteriostatic water during preparation. Some injections require preservative-free solutions for immediate single-dose use. Understanding medication requirements prevents improper dilution practices. Healthcare professionals select the appropriate injection diluent based on specific instructions. Some drugs require sterile water without preservatives for safe administration. Others require bacteriostatic water for multi-dose or repeated use situations. Correct selection ensures medication stability and patient safety. Professionals compare preparation options to match clinical needs accurately. This process supports consistent dosing and reduces preparation errors. Choosing the right reconstitution solution ensures correct medication delivery.
Understanding USP Grade Water Standards
USP grade water undergoes rigorous testing to confirm sterility and purity. These standards ensure the absence of harmful contaminants and endotoxins. Healthcare professionals rely on USP compliance during injection preparation decisions. Verified standards support safe reconstitution and injection practices. Manufacturing processes must meet strict regulatory guidelines consistently. Preservative levels remain carefully controlled under USP requirements. Clinicians trust USP grade water for reliable and predictable preparation outcomes. This trust supports safer patient care across multiple healthcare settings.
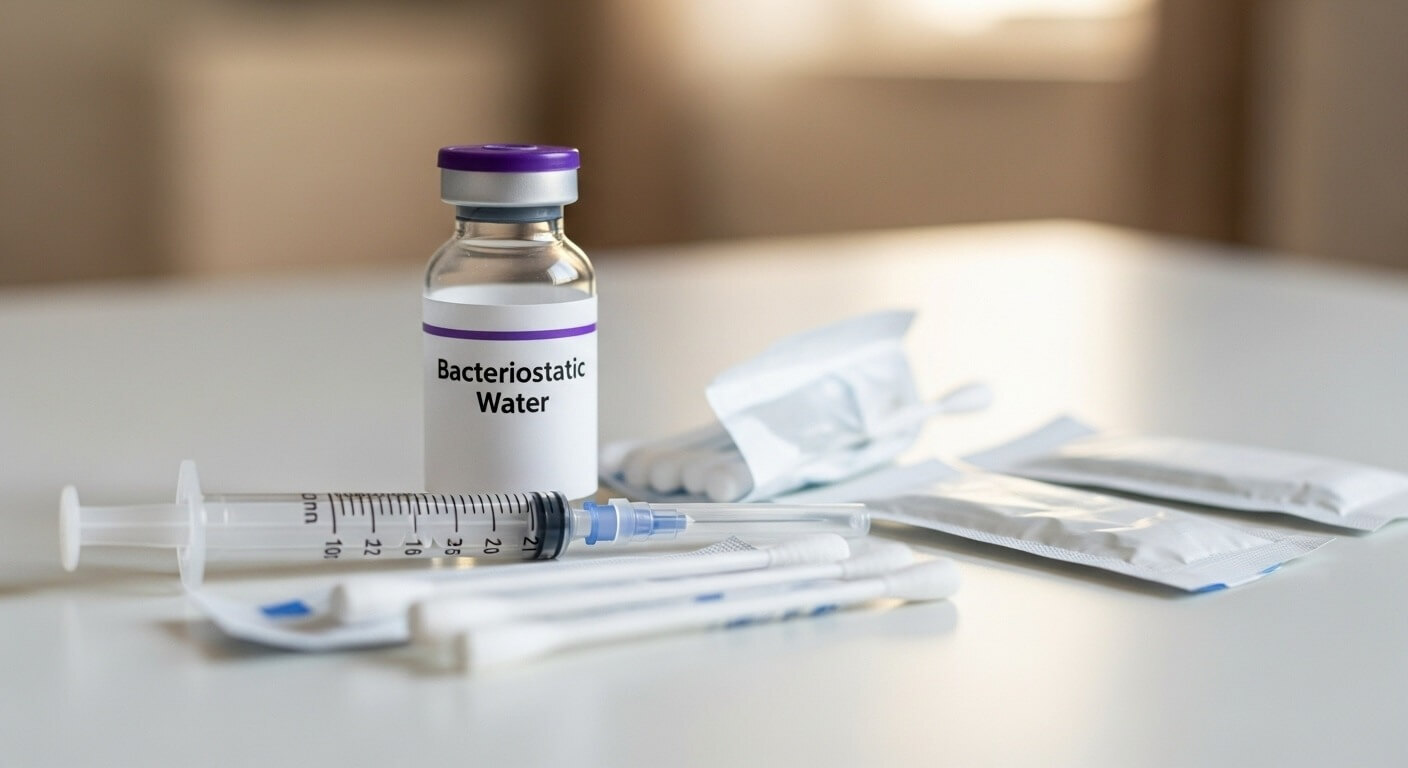
Conclusion
Choosing bacteriostatic water requires understanding formulation, use cases, and compliance standards. Healthcare professionals manage frequent injections across hospitals, clinics, and home care settings. Correct BAC water selection helps maintain safety and preparation accuracy. Verification of USP grade water ensures quality and patient protection. Understanding usage guidelines supports consistent outcomes during injection procedures. These informed choices improve clinical efficiency and patient confidence.
Reviewing handling guidelines before using bacteriostatic water is very helpful for healthcare providers. Knowledge of storage, withdrawal and application guarantees the long-term safety of solutions. There are evidence-based guidelines that caregivers are required to follow in preparing injections at home. This informed approach is helpful in serving safer practice and improved patient outcomes.

