Safe Storage Practices for Sterile Water
Feb 2nd 2026
All medical procedures start with preparation and storage is a silent yet very vital part. Sterile water facilitates injections, rinsing of devices and irrigation in healthcare settings on a daily basis. Its safety depends entirely on correct handling from delivery through final clinical use. As opposed to drinking water, sterile water should never contain any microorganisms. Storing them improperly enhances the risks of contamination and undermines the ability to protect patients in routine procedures.
Hospitals and clinics rely on strict sterile water storage standards in order to ensure consistent care results. The sterile water passes through various handling steps until it gets to the clinical workspace. All these steps would cause possible exposure in case of poor control of storage conditions.
Clean environments and organised storage reduce risks and support infection prevention goals. Medical staff consider specific storage protocols in order to maintain the effectiveness and sterility. These guidelines protect patients and other medical staff against avoidable complications. Regulatory compliance and increased trust in daily clinical practices are guaranteed by safe storage. Understanding proper storage builds confidence and supports safer medical decision-making environments.
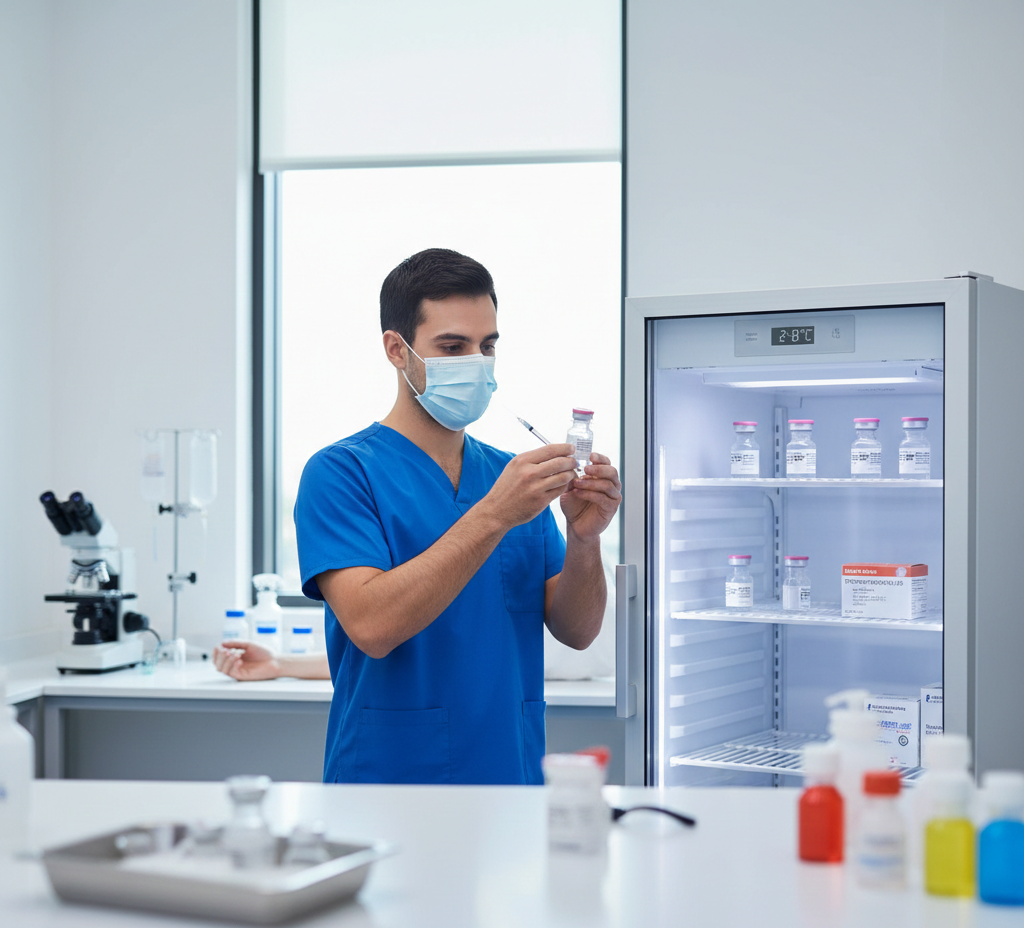

How to Safely Store Sterile Water for Injection
This medical-grade water for injection must remain sealed until the moment of use. Opening containers early increases contamination risk and reduces sterility assurance. Healthcare teams must treat unopened containers as protected medical products. Storage facilities should be kept clean and dry separating from any biological materials. Specialized shelves contribute to the minimization of accidental exposures or incorrect handling of products.
Facilities often store water for injection alongside other preparation solutions. Clear labelling and organised placement reduce handling errors during busy clinical workflows. Staff should avoid storing medical-grade water near sinks or waste disposal areas. High-risk zones increase airborne contamination and handling mistakes.
Aseptic handling begins with proper storage location selection. Clean cabinets support safe access and controlled product movement. Staff training reinforces correct storage habits and accountability. Correct storage ensures sterile medical water remains reliable for safe clinical administration.
Recommended Temperature and Conditions
Temperature stability plays a major role in preserving medical-grade water integrity. Most manufacturers recommend controlled room temperature for optimal product safety. This temperature’s range typically remains within twenty and twenty-five degrees Celsius. Extreme heat can weaken general seals on the containers and increase the risks of contamination. Cold temperatures may cause container stress or material damage.
Stable conditions protect packaging integrity throughout storage duration. Sterile medical water must not be exposed to direct sunlight. The packaging materials can be degraded by the ultraviolet light over extended periods. Storage rooms must be clear of strong chemical vapours.
Chemical fumes increase contamination risk and compromise product safety. Controlled environments support medical diluent safety standards across healthcare inventories. Consistent monitoring ensures products remain within acceptable environmental conditions. Appropriate conditions preserve sterility until clinical use occurs.
Single-Use Guidelines
Most medical-grade water products are intended for one-time access only. Once punctured, containers face immediate contamination risk from environmental exposure. Facilities must treat opened containers as single-use water sources. Medical staff must always use sterile syringes and needles. Opening the containers with non-sterile surfaces exposes the equipment to unsafe microorganisms.
The immediate disposal prevents the risk of accidental reuse and infection. Even multi dose containers have their strict aseptic handling protocols. Remaining products must follow facility-specific disposal guidelines after access. Staff should never save opened sterile medical water for later use.
These practices differ from preserved solutions designed for repeated access. Understanding this difference supports safe reconstitution solution handling practices. Single-use discipline protects patients from avoidable clinical infections. Strict adherence supports safety and regulatory compliance.
Avoiding Contamination and Spoilage
The medical-grade water has no expiry or does not spoil like food however; contaminated water is unsafe. Contamination usually occurs by way of poor handling or inappropriate storage conditions. Awareness facilitates the minimization of avoidable clinical safety incidents. Common contamination risks include:
- Exposure to open air during improper handling
- Contact with non-sterile surfaces or tools
- Reusing containers without preservatives
Clean storage cabinets reduce exposure to dust and airborne spores. Staff should avoid placing sterile medical water near sinks or waste areas. Environmental controls support ongoing sterility maintenance. Understanding differences between sterile and preserved solutions improves safety. Sterile water lacks preservatives and requires strict aseptic technique. Consistent handling protects product integrity and patient outcomes. Contamination prevention begins with disciplined daily storage practices.
Shelf Life and Expiry Awareness
Every medical-grade water container displays a clearly marked expiry date. Manufacturers guarantee sterility only until that printed date. Facilities must respect these limits for safe clinical practice. Expired products may appear normal but lack sterility assurance. Using expired water increases infection and compliance risks. Routine inventory checks prevent accidental use of expired products. Facilities should rotate stock using first-in, first-out methods. Visual inspection helps identify damaged or compromised containers. Bulging or broken seals indicate disposal requirements.
Regular audits support compliance and reinforce storage discipline. Expiry awareness strengthens overall sterile water storage management systems. Proper monitoring protects patients and healthcare providers alike. Expiry control remains a fundamental safety responsibility.
Sterile Water for Irrigation and Antiseptics
The purified sterile solution used for irrigation follows similar storage requirements. Unopened containers still require controlled temperature and clean environments. Irrigation products often experience more frequent handling. Once opened, irrigation containers should be used promptly. Delayed use increases microbial growth risks on exposed surfaces. Facilities must follow infection control disposal timelines. Irrigation often involves contact with open wounds or tissues. This increases the importance of proper handling and storage discipline. Clean technique protects vulnerable patients during procedures.
Although antiseptics differ, sterile water requires stricter controls. Correct storage supports safety beyond injection-related applications. Irrigation use reinforces disciplined sterile handling principles. Safe storage protects patients across multiple clinical uses.

Conclusion
Safe storage practices protect sterile medical water throughout its clinical lifecycle. Controlled temperatures, clean environments, and strict handling preserve sterility. These steps directly support patient safety and procedural effectiveness. Healthcare environments rely on consistent storage discipline daily. Proper practices reduce infection risks and regulatory violations. Every handling step contributes to safe medical outcomes. Disciplined storage habits support confidence in clinical workflows. Medical-grade water safety depends on consistent attention and responsibility. Good storage protects both patients and healthcare professionals. Simple practices make meaningful safety differences every day.
Consistent storage and handling habits protect sterile water integrity. Simple practices reduce contamination risks and improve clinical confidence. Commitment to correct storage supports safer patient care outcomes.
Better care begins with better choices. Explore trusted healthcare solutions, rely on the right medical diluent for precise preparation, and use proven options like Hospira sterile water to support safety, accuracy, and confident clinical outcomes every day.